In vitro diagnostic industry overview
1. Industry Overview
1.1 Definition
In Vitro Diagnosis (IVD) refers to the detection and verification of human samples (blood, body fluids, tissues, etc.) by using in vitro detection reagents, instruments, etc., in addition to the human body, to obtain clinical diagnostic information. The process of prevention, diagnosis, treatment testing, post-observation, health evaluation, and genetic diseases. The in vitro diagnostic industry belongs to the pharmaceutical biotechnology industry.
1.2 Classification
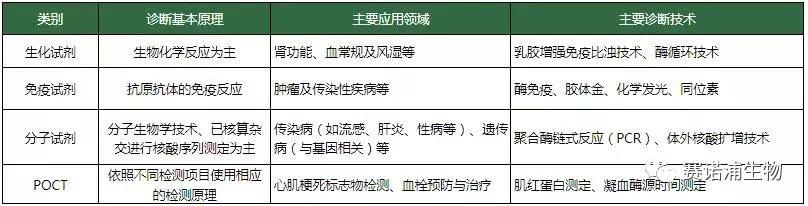
1) In vitro diagnostic equipment
According to the diagnostic method: clinical chemical analysis equipment, immunochemical analysis equipment, blood analysis equipment, microbiological analysis equipment.
2) In vitro diagnostic reagents
According to the principle of inspection: biochemical diagnostic reagents, immunodiagnostic reagents, molecular diagnostic reagents, microbial diagnostic reagents, urine diagnostic reagents, blood coagulation diagnostic reagents, hematology and flow cytological diagnostic reagents.
2. Industry policy
2.1 Administrative authorities
2.1.1 National Drug Administration
The administrative department in charge of the in vitro diagnostic industry is the State Drug Administration. National in vitro diagnostic reagents for blood source screening, in vitro diagnostic reagents labeled with radionuclides are in accordance with drug management, and other in vitro diagnostic products are managed by medical devices. In terms of quantity, the varieties that are classified as medical devices account for the vast majority. The specific management department of the in vitro diagnostic industry is the Medical Device Supervision Division. Its basic functions include supervision of the in vitro diagnostic industry, release and implementation of national and industry standards, product market access, production enterprise qualification, product advertising, product clinical trials and product registration. Approval, etc.
2.1.2 Clinical Inspection Center of the Ministry of Health
The Clinical Testing Center of the Ministry of Health is the permanent institution of the National Clinical Testing Standardization Committee of the Ministry of Health. It is mainly responsible for formulating clinical testing technical standards and management norms; responsible for quality management, technical guidance, quality evaluation of clinical testing instruments, and establishment of reference methods for clinical testing in the country. , the establishment of calibration laboratories, technical training for clinical laboratory professionals, etc.
2.1.3 Industry Association
The self-regulatory organization of the in vitro diagnostic industry is the China Medical Device Industry Association In vitro Diagnostic System Professional Committee (referred to as the 'IVD Special Committee'). The IVD Committee is mainly responsible for market research in the in vitro diagnostic industry, participation in the formulation of relevant industry standards and policies and regulations, public services for member companies, industry self-discipline management, and industry development proposals for government members on behalf of member companies.
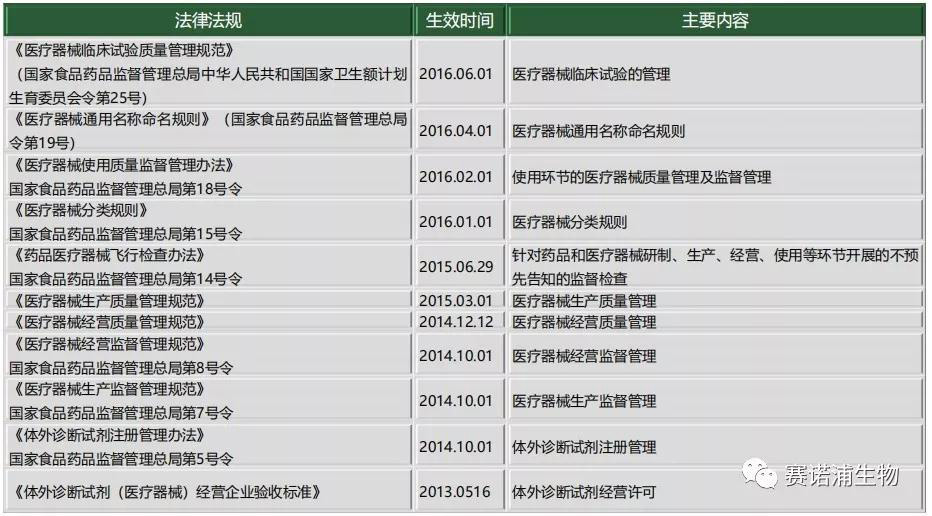
2.2 Laws and regulations
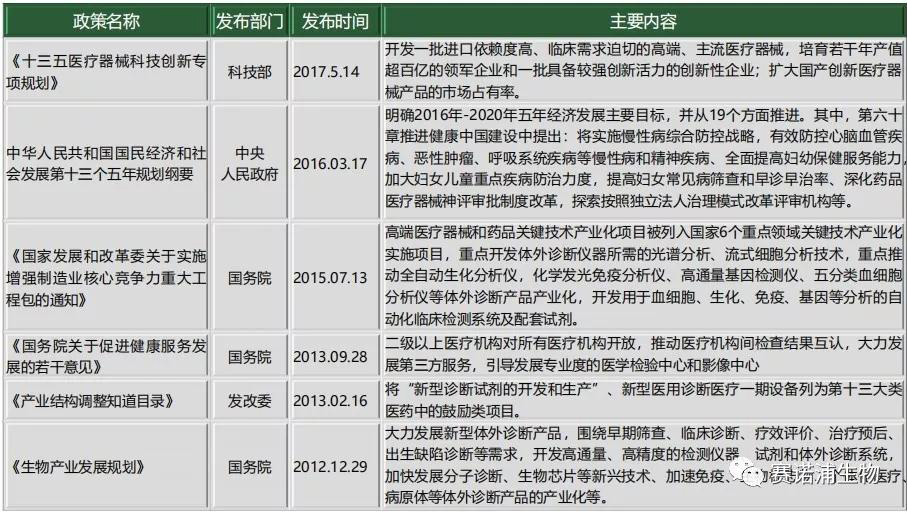
2.3 Industrial Policy
3. Industry development process
After long-term accumulation in China's in vitro diagnostic industry, the development history of domestic IVD can be divided into four stages: market introduction period, early growth stage, rapid development period and upgrade replacement period.

4. Industry development status
4.1 Business diversification
Segmentation: Enterprises that already have competitive advantages rely on their own resources to penetrate into other segments, thus enriching the product line structure;
Reagent production enterprises: increase the production of instruments, or increase the production of reagents by instrument manufacturers, thereby enhancing market competitiveness through bundled sales;
Enterprises with a certain market share: actively expand overseas markets on the basis of occupying a certain market share in China;
Some third-party inspection laboratories: established and developed one after another;
Non-IVD industry commercial enterprises: Through the hospital commissioned consumables procurement and integrated sales channels to cross the border into the IVD industry, quickly seize market share.
4.2 Industry M&A integration is active
Since 2015, in order to adapt to the trend of centralized procurement and drug consumables two-vote system in medical institutions, M&A integration in in-vitro diagnostic industry is very active.
Distribution channel companies such as Runda Medical (603108.SH) and Ceriss (603716.SH) continue to acquire and integrate high-quality agents in the channel; on the other hand, expand the industry to upstream production through the acquisition of IVD production enterprises. chain.
Reagent manufacturers such as Meikang Bio (300439.SZ) and Mike Bio (300463.SZ) will increase their investment in product R&D, and expand downstream through M&A channel agents to improve terminal customer control.
Pharmaceutical commercial enterprises such as Ruikang Medical also cross-border participation in the merger and acquisition of IVD consumables channels to further increase market share.
4.3 Industry capital market is active
In 2017, there were 8 companies listed in the IVD industry. At present, there are 26 in vitro diagnostic related companies listed on the A-share market. Among them, Mindray Medical has a market value of over 100 billion yuan since its listing in 2018. It is the largest medical device manufacturer in China. There were 100 financing incidents in 2018, and the financing scale reached nearly 7 billion yuan.
5. Industry scale
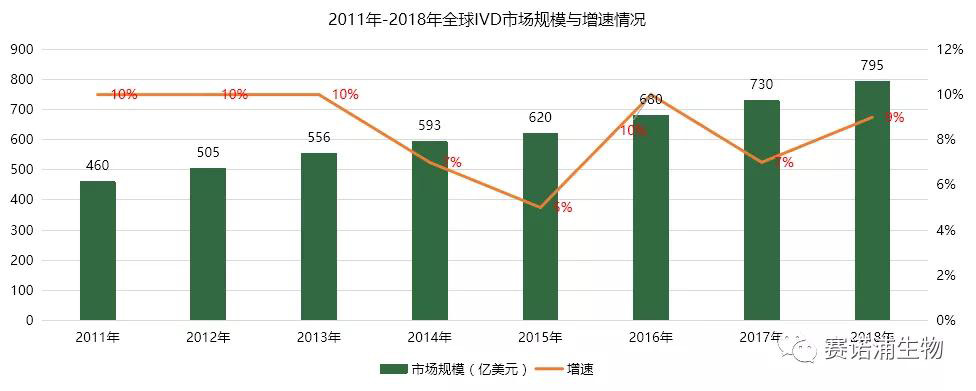
5.1 International market size
The global in vitro diagnostic market has maintained a steady development trend. In 2015, the global in vitro diagnostic market was about US$62 billion, reaching US$79.5 billion in 2018, and the compound growth rate was 7% from 2015 to 2018. Developed countries such as Europe and the United States are the main markets for in vitro diagnosis. According to IVD Technology, the United States, Western Europe and Japan are the world's top three in vitro diagnostic markets, with market shares of 41%, 25%, and 9% respectively. The developed markets are relatively mature and developing. More stable.
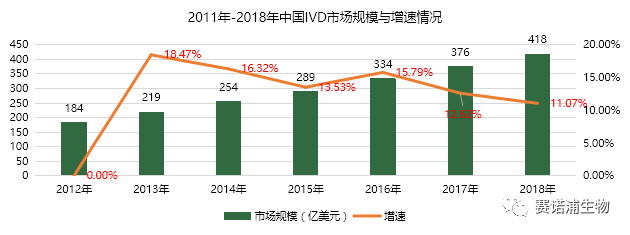
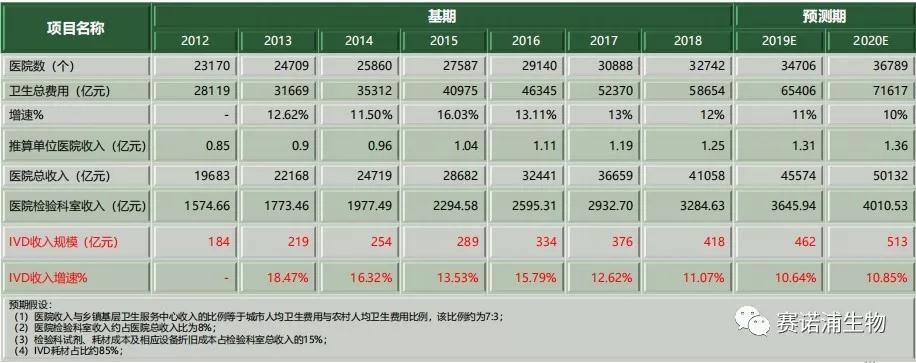
5.2 China market size
The growth rate of China's in vitro diagnostic industry has remained between 11% and 16% and is increasing year by year. In 2018, the income of China's in vitro diagnostic industry was about 41.8 billion yuan. It is expected to reach 51.3 billion yuan in 2020.
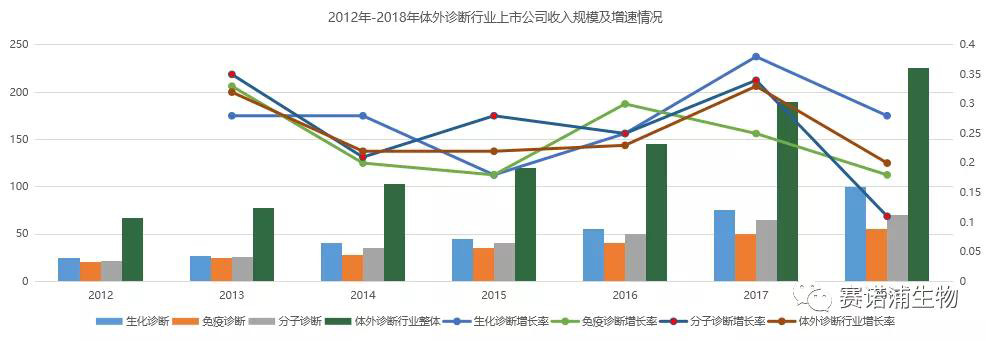
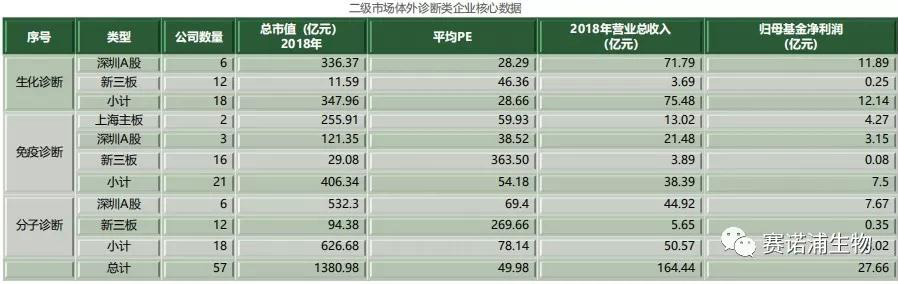
There are currently 57 listed in vitro diagnostic companies in China. Among them, there are 17 listed companies on the Main Board and 40 listed companies on the New Third Board. The in vitro diagnostic listed company's revenue in 2018 is about 20 billion yuan, accounting for about 45% of the total industry scale. Biochemical in vitro diagnostics listed companies account for a relatively large proportion of income, which is mainly related to the early development of the company. The relative concentration of the listed companies in the immune and molecular diagnostics is relatively small, and the corresponding listed companies have relatively small income scale.
6. Industry drivers
6.1 China's population is aging
The market size of in vitro diagnostics is directly related to the amount of medical diagnosis and treatment. The aging population brings about an increase in medical demand. With the increase of the number of tests, China is about to enter an aging society. By the end of 2016, there were 230 million elderly people over 60 years old in the country, accounting for the total population. 16.7% of the population, including 150 million people over the age of 65, accounting for 10.8% of the total population. According to the 2015 Global Report on Ageing and Health, published by the World Health Organization, it is estimated that the number of elderly people in China will increase from 194 million to 485 million in 2012-2050, and the level of aging will increase from 14.3% to 34.1%. The aging population has increased the level of economic development, resulting in steady and rapid growth in per capita health expenditures, laying a good foundation for the development of the in vitro diagnostic industry.

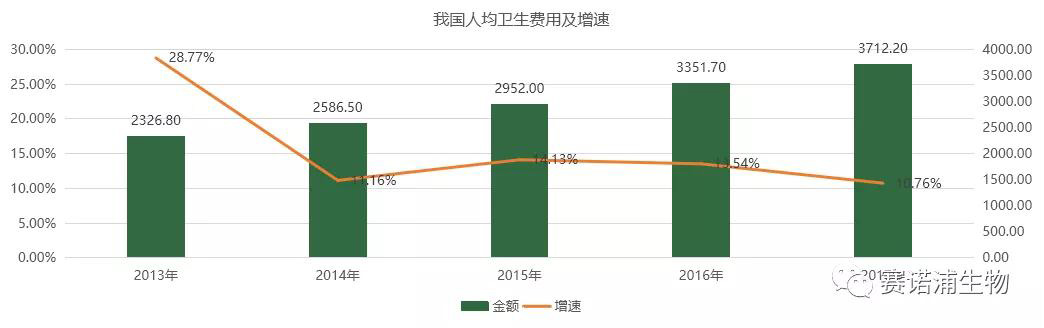
6.2 China's per capita health expenditures maintain rapid growth
According to the statistical yearbook data, since 2011, the income level of urban residents in China has grown rapidly, and by 2017, the per capita disposable income has increased by about 40 times. The aging population is superimposed on the level of economic development, resulting in a steady increase in per capita health expenditures.
6.3 Policy promotion for medical insurance control, graded diagnosis and treatment, etc.
After the public hospital reform was further proposed, the drug revenue in 2017 fell below 30%. Improving the level of medical services and medical diagnosis has become an inevitable trend in hospital development. IVD is a prerequisite for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Compared with the inspection of large-scale imaging equipment, the price is low, the proportion of medical expenses is small, and the patient's sensitivity to examination costs is low. Therefore, the investment in in-vitro diagnosis is increasing the hospital's continuous improvement of medical services and diagnosis and treatment. An important means, medical in vitro diagnostic needs will maintain a rapid growth trend in the future.
Medical insurance control fees have led to a constant rebalancing between inspection quality and cost control. Domestic high-quality IVD products have gradually gained import substitution opportunities, and the policy has accelerated the import substitution process. In the primary hospitals, the grading diagnosis and treatment policy has led to an increase in the number of primary and secondary hospitals. On the one hand, the demand for basic testing equipment has gradually increased. The small reduction in inspection prices has far less impact on domestically produced IVD faucets than on imported alternatives and grading clinics.
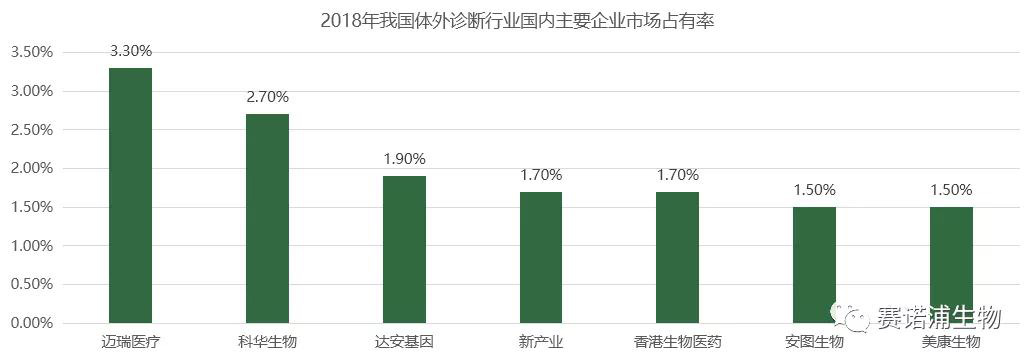
6.4 Import substitution space is huge
China's in vitro diagnostic industry is mainly based on the midstream reagents and instruments of the core of the industrial chain. It has achieved localization to a certain extent in various sub-sectors, and the localization rate is still low in some high-end fields. At present, the localization of reagents is faster than the instrument. In the production process of the instrument, some low-end instruments have been localized, and most high-end instruments rely on imports. In the domestic in vitro diagnostic market in 2018, imported instruments and reagents accounted for more than 50% of the share. In the future, with the technological breakthroughs of domestic enterprises, import substitution will provide a huge market space for domestic enterprises.
6.5 Prevention of infectious diseases promotes the development of diagnostic reagents
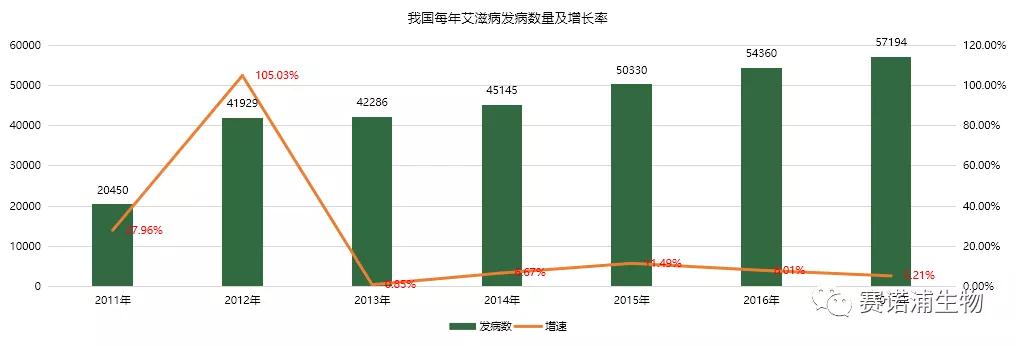
Infectious diseases represented by hepatitis and AIDS continue to be highly prevalent in China. According to the 2017 Statistical Bulletin on the Development of Health and Family Planning in China, a total of 2.957 million cases of infectious diseases were reported in the national Class A and B infectious diseases in 2017, and the deaths were reported. 17,968 people, including 122.15 million cases of viral hepatitis, accounting for 41.3% of the total number of cases, the highest incidence of all infectious diseases. The AIDS epidemic, although the base is small but growing rapidly, the average incidence growth rate in the six years from 2011 to 2017 is 70%.
In vitro diagnosis has obvious advantages in the detection and prevention of infectious diseases. The rise of the incidence of infectious diseases has greatly promoted the development of the in vitro diagnostic industry. As the country continues to increase its control over infectious diseases, it will further promote the in vitro diagnostic market. development of.
6.6 China's new cancers rank first in the world, and the demand for gene sequencing market is expanding
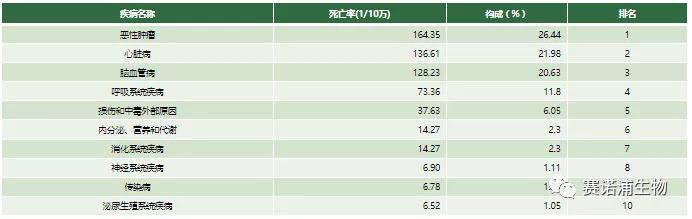
The global incidence of cancer is growing, and China ranks first in the world. According to the World Health Organization's (WHO) Global Cancer Report, global cancer cases are on the rise. Nearly 50% of new cancer cases have occurred in Asia, and China has the highest number of new cancer cases in the world. Among the top ten causes of death among urban residents in China in 2017, malignant tumors ranked first, and the mortality rate of malignant tumors was 164.35/100,000, accounting for 26.44%. The incidence of tumors is closely related to individual genetic information, and each person's genetic information is different. Therefore, individualized precision medicine is becoming the mainstream, and gene sequencing technology is an important part of individualized treatment of tumors. Under the situation that the incidence of tumors is gradually increasing, the molecular diagnosis represented by gene sequencing has great potential for development in China.
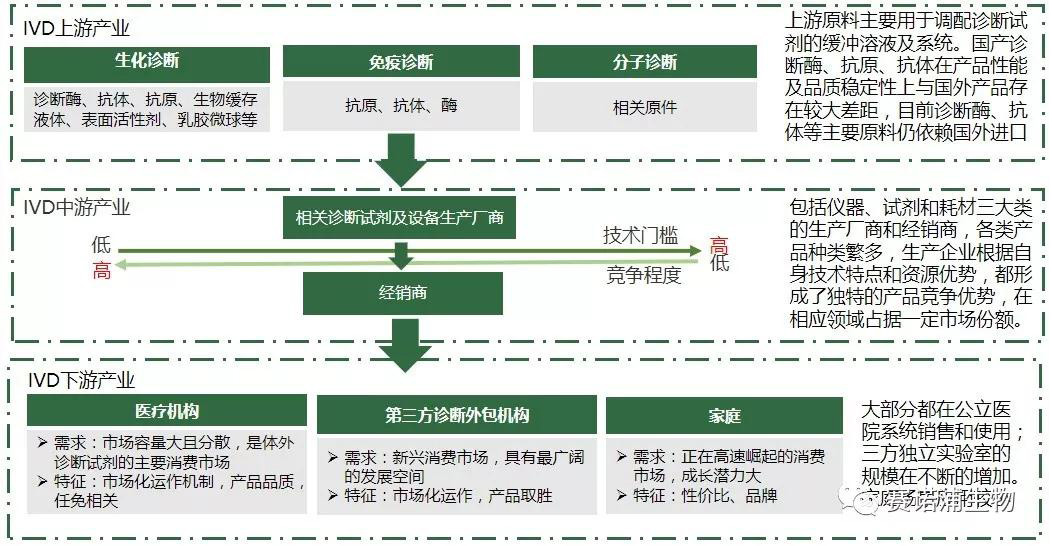
7. Industry chain
The in vitro diagnostics industry chain includes upstream raw material supply industry, midstream manufacturing industry and downstream application industry. The upstream raw materials industry provides biochemical raw materials, including biological products such as diagnostic enzymes, antigens and antibodies. The downstream demand mainly comes from medical testing and blood screening. At present, medical testing is the most important direction of in vitro diagnosis.
8. Business model
The business model of the in vitro diagnostic industry is relatively simple, and manufacturers mainly obtain benefits by producing and selling in vitro diagnostic products to customers.
Pricing is subject to bidding mode. Medical and health institutions in various regions generally entrust an independent third party to bid for the diagnostic reagents to be purchased annually. After winning the bid, the manufacturer can sell the products in the region according to the price range.
The sales model is based on dealer sales, supplemented by direct sales.
8.1 business model

8.2 sales model

(To be continued...)